Azure Application Gateway Concepts
Understand the core concepts behind Azure Application Gateway, a web traffic load balancer that enables you to manage traffic to your web applications.
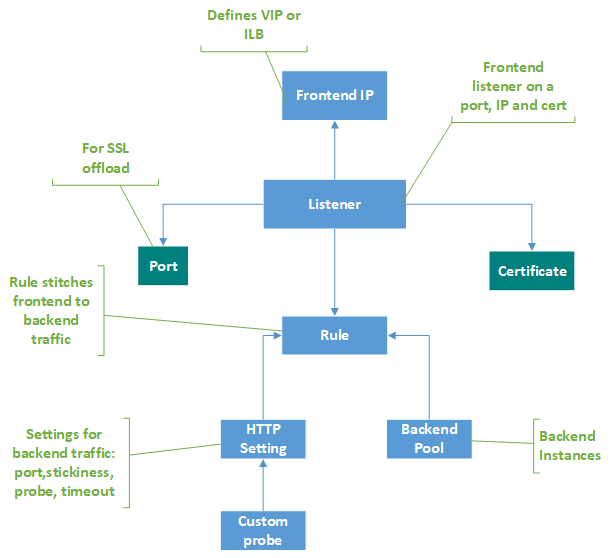
Frontend IP Configuration
This defines the IP address(es) that Application Gateway listens on for incoming traffic. You can configure it to use a public IP address, a private IP address, or both.
- Public IP: For internet-facing applications.
- Private IP: For internal applications within your VNet.
Listeners
A listener is a logical entity that checks for connection requests based on the IP address, port, and protocol. It’s configured with a frontend IP configuration and defines how traffic enters the Application Gateway.
- Supports HTTP and HTTPS.
- Can be configured for multi-site hosting.
Rules
Rules define how to route incoming requests to backend pools. There are two types of rules:
- Basic Rule: Routes traffic directly to a backend pool without complex routing logic.
- Path-based Routing Rule: Allows you to route requests to different backend pools based on the URL path of the request.
Backend Pools
A backend pool contains the virtual machines, virtual machine scale sets, or web apps that receive traffic from Application Gateway. You can have multiple backend pools associated with different rules.
HTTP Settings
HTTP settings define how Application Gateway connects to the backend pool. This includes details like the backend port, protocol (HTTP or HTTPS), cookie-based affinity, connection draining, and health probe settings.
- Cookie-based affinity: Ensures a user’s requests are always sent to the same backend server.
- Connection draining: Gracefully removes backend servers from service.
Health Probes
Health probes are used to monitor the health of backend servers. Application Gateway periodically sends probes to backend servers, and if a server fails to respond within a defined threshold, it's marked as unhealthy and traffic is rerouted.
- Configurable probe interval, timeout, and threshold.
- Supports custom probe paths.
Simplified Application Gateway Architecture
SSL Offloading
Application Gateway can decrypt incoming HTTPS traffic, saving backend servers from the overhead of SSL encryption/decryption. The traffic between Application Gateway and the backend can then be unencrypted HTTP.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Optionally, Application Gateway can include a Web Application Firewall to protect your web applications from common web vulnerabilities and exploits, such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
Session Affinity (Cookie-Based Affinity)
When enabled, Application Gateway inserts a cookie into the response to the client. Subsequent requests from the client containing this cookie will be routed to the same backend server. This is useful for applications that require session persistence.